Capes, Cameras, and the Cult of Visibility: The SeaLight Crusade as White Savior Theater
By Tina Antonis
The South China Sea is more than a maritime dispute—it’s a theater of narrative warfare. While headlines focus on Chinese aggression and Philippine resistance, a quieter campaign unfolds in the background: one of satellite feeds, curated imagery, and Pentagon-backed storytelling. At the center of this effort is SeaLight, a project that claims to illuminate truth but often casts shadows of its own.
As explored in my article at Antiwar.com, SeaLight doesn’t just document—it performs. It reframes geopolitical tension through moral spectacle, positioning its creators as heroic arbiters of transparency. But when the messenger wears a cape and the funding flows from defense budgets, we must ask: is this clarity, or choreography?
Stage Left: The White Savior Enters
In the comic-strip cosmology of Ray Powell’s SeaLight project, transparency wears a cape. Clad in heroic postures and backed by satellite imagery, Powell casts himself as the guardian of maritime morality—unarmed, except with satellite feeds, theatrical flair, and strategic messaging.
Yet beneath the cartoon and Pentagon-funded optics lies a familiar archetype: the white savior, rebranded for the South China Sea.
China Is Imperialist? Says Who?
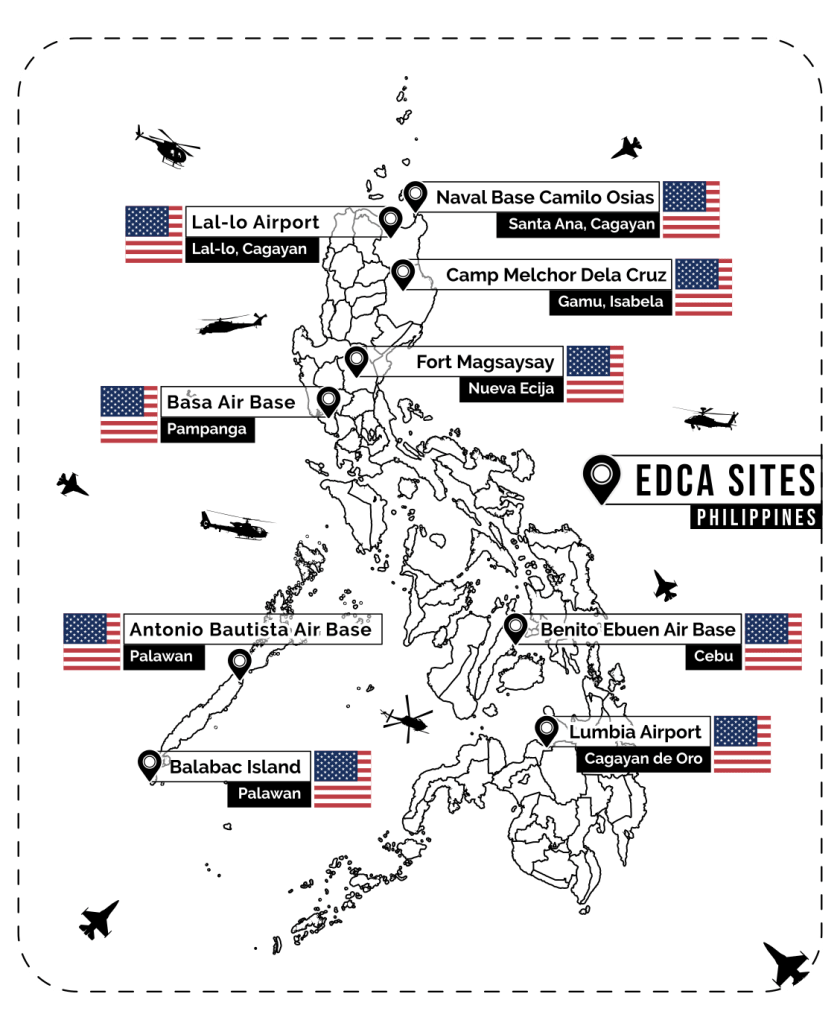
Calling China a “maritime occupier,” Powell positions himself as a bulwark against aggression. But that moral pose collapses under scrutiny. He speaks for a country with over 800 foreign military installations and a documented history of over 250 military interventions since 1991—wars in Iraq, Afghanistan, Libya, Syria, Somalia, and dozens more, all under the banner of peace, freedom, or preemption.
By comparison, China’s post–Cold War footprint includes no sustained foreign occupations and only scattered border conflicts and peacekeeping missions. The imbalance is staggering. And Powell’s framing doesn’t just ignore it—it performs around it.
As David Vine argues in The United States of War, this vast base empire is not a passive network—it’s an architecture of perpetual war. These outposts make military engagement not an exception but a structural habit, cloaked in strategic necessity and sold as global stewardship.
Powell’s cartoon rhetoric—calling China an occupier—obscures the scale of U.S. militarism. The term “occupation” is deployed not to analyze, but to project. When adversaries hold territory, it’s a crisis; when the U.S. spans the globe with armed installations, it’s policy.
Framing Conflict: The Optics of Consent
This isn’t irony. It’s performance. Powell’s language manufactures a moral frame for confrontation—costumed in transparency, but driven by escalation. The cape is literal. The conditioning is deliberate. And the stage is set for war.
SeaLight’s mission is not just visual documentation—it’s narrative warfare. As the Japan Times openly notes, its “chief weapon is photography, applied purposefully, generously and consistently over time.” These images—enhanced, curated, and distributed across media—are not neutral. They’re constructed to shape public perception, sway international opinion, and ultimately manufacture consent for confrontation.
Assertive transparency becomes a kind of ideological scaffolding—a stage on which geopolitical tension is dramatized, simplified, and morally polarized. The goal isn’t simply to reveal conflict; it’s to condition audiences for escalation.
And when the messenger dons a superhero’s cape, the spectacle transforms into something deeper: a story of rescue, of virtue, of intervention. This is not analysis—it’s soft propaganda dressed in heroic metaphor.
Consent for war doesn’t begin with missiles. It begins with mythmaking.



You must be logged in to post a comment.